Abstract
The adsorption of ionic surfactants on the water/air or water/hydrocarbon interface is considered. One form of the well-known Gibbs equation takes into account the surface excess of the amphiphilic ion in the compact layer, or monolayer, Γm2 (2D adsorption), and the differential of the electrical potential of this layer. This expression is modified using some simplifying assumptions. The dependence of the surface tension, σ, on the activity of the amphiphilic ion, a2, degree of gegen-ions binding in the compact layer, β, and Γm2 is transformed into the following relationship:
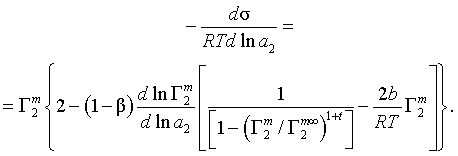
Here Γm∞2 denotes the Γm2 value at complete filling of the adlayer, t = –1, 0, or +1 for the two-phase model of partition, for immobile or mobile monolayer respectively, b is the cohesion constant; both the long-tailed ion and the gegen-ion are single-charged. The usefulness of the proposed equation is discussed.
Keywords: water/air interface, adsorption of ionic surfactant, surface tension, adsorption in the monomolecular layer, degree of gegen-ions binding.
УДК 541.18.04